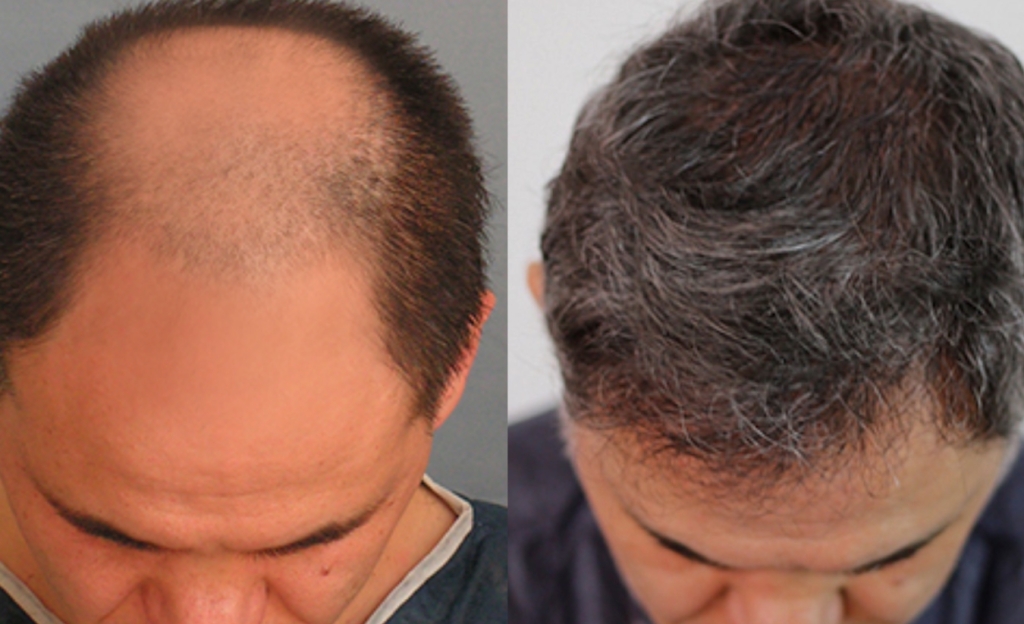
Hair transplant surgery can help those struggling with hair loss to restore a full head of hair. It works by taking hair follicles from an area of the scalp with an abundant supply of hair and transplanting them into balding or thinning areas.
Hair transplant surgery is a minimally invasive procedure, typically performed in an outpatient setting. It involves removing healthy hair follicles from the back of the head, and then transplanting them into areas of baldness or thinning. Because the donor area is not affected by hair loss, the transplanted hair should remain for a lifetime.
The surgery is usually done under sedation or local anesthesia, so that the patient is comfortable during the procedure. The operation usually takes between four hours and eight hours, depending on the number of grafts that need to be transplanted. During the operation, the hair follicles are carefully removed from the donor area and placed into incisions made in the balding or thinning areas.
The transplanted hair should start to grow within a few weeks after the surgery, and the results will become noticeable within six to eight months. The transplanted hair may initially appear thin, but it will gradually start to thicken as it matures and matures.
Although hair transplant surgery is generally safe and effective, there are some risks associated with the procedure. Infection, scarring, and bleeding are the most common problems, which are usually minor and can be treated with antibiotics. Numbness or tingling of the scalp can also occur, and the transplanted hair may not grow as thick as the patient desires.
Hair transplant surgery can be a great option for those who are suffering from hair loss. It can restore a full head of hair and improve the patient’s self-confidence. However, it is important to discuss all of the risks and benefits of the procedure with a qualified surgeon before undergoing the surgery.